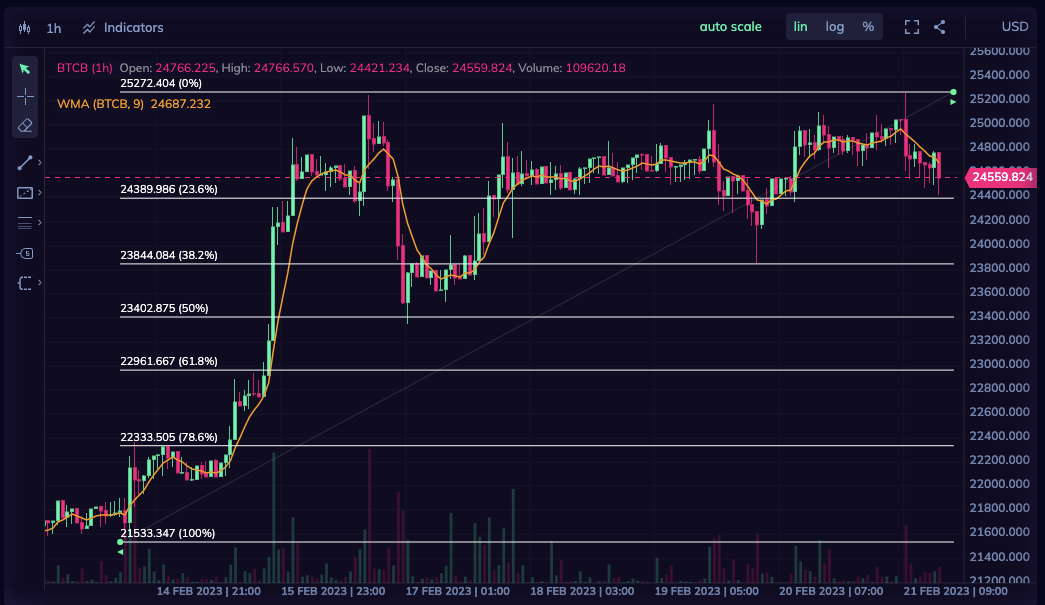
Ethereum (ETH).
Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain platform that enables developers to build and run decentralized applications, known as dApps, without any central authority.

Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain platform that enables developers to build and run decentralized applications, known as dApps, without any central authority. It is a decentralized open-source blockchain, much like Bitcoin, that allows developers to build smart contracts and execute them on the blockchain.
History of Ethereum
Ethereum was created in 2013 by Vitalik Buterin, a Canadian-Russian programmer. He was inspired by Bitcoin's blockchain technology and decided to create a more advanced blockchain with more features. Buterin started to write the Ethereum white paper in November 2013, and the project was officially announced in January 2014.
Ethereum held its first crowdsale in July 2014, which raised over $18 million worth of ether, the platform's native cryptocurrency. The Ethereum network went live on July 30, 2015, with 72 million ethers issued in the crowdsale.
Numbers
Currently, Ethereum is the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, with a market cap of over $200 billion as of March 2023. The platform has over 200,000 active developers working on it and over 2,000 dApps running on its network.
As of March 2023, the current block reward for mining on the Ethereum network is 2 ETH per block. The total supply of ether is not capped, and there are currently over 120 million ethers in circulation.
Use Cases
The Ethereum platform enables developers to build decentralized applications, which can be used in various industries. Some of the use cases of Ethereum include:
- Decentralized finance (DeFi): Ethereum is the backbone of the DeFi industry, which allows users to access financial services such as lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries.
- Gaming: Ethereum enables developers to build decentralized games, where users can own in-game assets and trade them on a decentralized marketplace.
- Identity: Ethereum can be used to create a decentralized identity system, where users have control over their personal data.
- Supply Chain: Ethereum can be used to create a transparent supply chain system, where every transaction is recorded on the blockchain.
How it works
Ethereum uses a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus algorithm, similar to Bitcoin. Miners on the network compete to solve complex mathematical problems to add new blocks to the blockchain and receive a block reward in ether.
Smart contracts are the backbone of the Ethereum platform. Smart contracts are self-executing programs that automatically execute when certain conditions are met. They can be used to automate various processes, such as financial transactions, voting systems, and identity verification.
Interesting Facts
- Ethereum was not the original name for the platform. It was initially called "The Ethereum Project" and was later renamed Ethereum.
- The Ethereum network suffered a major hack in June 2016, which resulted in the loss of over $50 million worth of ether.
- In 2021, the Ethereum network underwent a major upgrade called Ethereum 2.0, which introduced a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus algorithm, replacing the PoW algorithm.
- The co-founder of Ethereum, Vitalik Buterin, is one of the youngest crypto billionaires, with a net worth of over $20 billion as of March 2023.
In conclusion, Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain platform that enables developers to build and run decentralized applications without intermediaries. It is the backbone of the DeFi industry and has numerous use cases in various industries. Ethereum has a vibrant developer community, and the platform is constantly evolving with new upgrades and innovations.