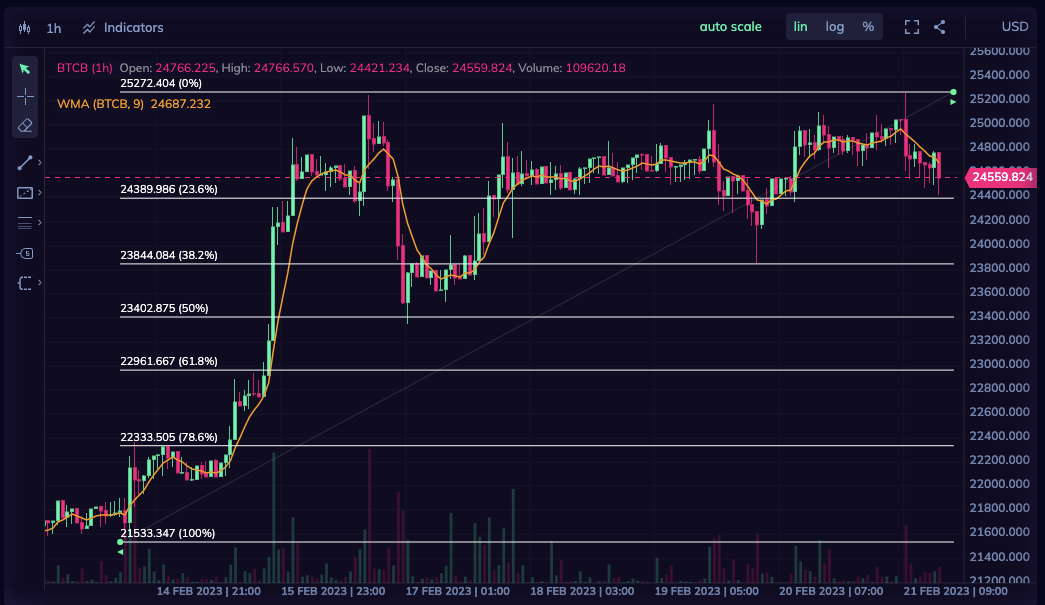
Layer 0, 1, and 2 in Crypto.
Layer 0, 1, and 2 are terms used in the world of cryptocurrency to describe different levels of technology and infrastructure that underpin the blockchain ecosystem.

Layer 0, 1, and 2 are terms used in the world of cryptocurrency to describe different levels of technology and infrastructure that underpin the blockchain ecosystem. Each layer has its own unique features and functions, and they work together to create a decentralized, secure, and scalable blockchain network.
Layer 0: Physical Layer
The physical layer, or Layer 0, refers to the physical infrastructure that underpins the blockchain network. This includes the hardware devices such as mining equipment and nodes that are used to power the network. The physical layer also includes the internet infrastructure that connects nodes and allows for communication between them. The physical layer is critical to the functioning of the blockchain network, as it provides the necessary resources to support the network.
Layer 1: Protocol Layer
The protocol layer, or Layer 1, refers to the basic rules and protocols that govern the blockchain network. It includes the consensus algorithm, which determines how transactions are verified and added to the blockchain. It also includes the rules for creating new blocks, validating transactions, and managing the blockchain network. Examples of Layer 1 protocols include Bitcoin's proof-of-work (PoW) consensus algorithm and Ethereum's proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus algorithm.
Layer 2: Application Layer
The application layer, or Layer 2, refers to the layer of the blockchain network where applications and smart contracts are built. It allows developers to create decentralized applications (dApps) that can run on top of the blockchain network. Examples of Layer 2 protocols include the Lightning Network for Bitcoin and the Plasma network for Ethereum. These protocols enable faster and cheaper transactions, and they can also increase the scalability and interoperability of the blockchain network.
Benefits of Layered Architecture
- Decentralization: The layered architecture of the blockchain network enables decentralization, which is a key feature of the blockchain ecosystem. By distributing control and responsibility across multiple layers, the network is less susceptible to centralized control and can operate more transparently and securely.
- Scalability: The layered architecture of the blockchain network enables greater scalability, as it allows for the creation of more complex applications and systems that can operate on top of the network.
- Interoperability: The layered architecture of the blockchain network enables greater interoperability, as it allows for different protocols and systems to work together seamlessly. This can lead to greater efficiency and functionality in the blockchain ecosystem.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Layer 0, 1, and 2 are important components of the blockchain ecosystem. The physical layer provides the necessary resources to support the network, the protocol layer governs the basic rules and protocols of the network, and the application layer enables developers to create dApps and other systems that can run on top of the network. By understanding the different layers of the blockchain network, we can gain a better understanding of how it works and how it can be used to create new applications and systems.