Hot and Cold Wallets.
Hot and cold wallets are two main types of cryptocurrency wallets that are used for different purposes. Hot wallets are used for day-to-day transactions and are more vulnerable to hacking and theft, while cold wallets are used for long-term storage and are more secure but more difficult to access.
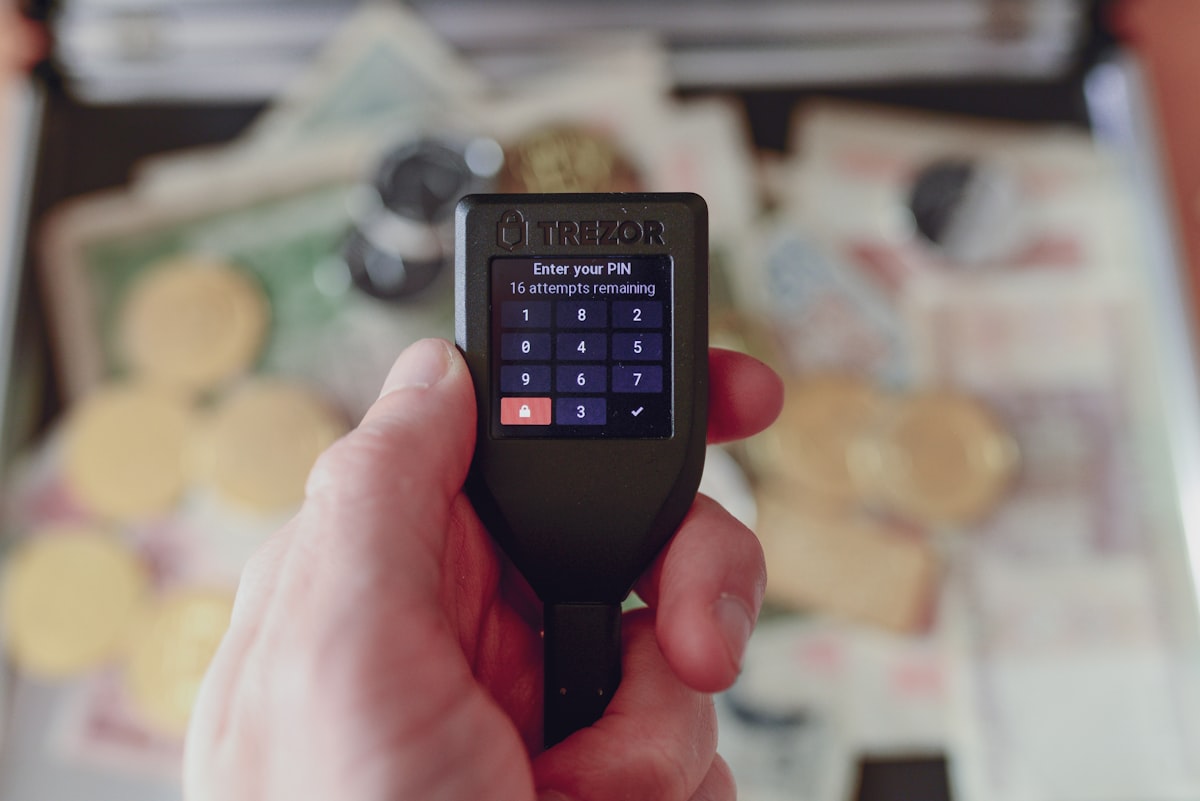

In the world of cryptocurrency, there are two main types of wallets: hot wallets and cold wallets. In this article, we will explore the definition, history, examples, how they work, and how to use them.
What is a Hot Wallet?
A hot wallet is a type of cryptocurrency wallet that is connected to the internet. This makes it easy to access and use, but also makes it more vulnerable to hacking and theft.
Hot wallets are typically used for day-to-day transactions, such as buying and selling cryptocurrencies. They are often built into cryptocurrency exchanges and can be accessed through a web browser or mobile app.
What is a Cold Wallet?
A cold wallet is a type of cryptocurrency wallet that is not connected to the internet. This makes it more secure than a hot wallet, but also makes it more difficult to access and use.
Cold wallets are typically used for long-term storage of cryptocurrencies. They are often in the form of a hardware wallet, which is a physical device that stores your private keys offline.
History of Hot and Cold Wallets
The concept of cryptocurrency wallets dates back to the creation of Bitcoin in 2009. In the early days of Bitcoin, there were few options for storing cryptocurrency securely. As a result, many early adopters stored their Bitcoin on exchanges, which were vulnerable to hacking and theft.
Over time, hot and cold wallets were developed as a way to store cryptocurrencies more securely. Hot wallets were developed to make it easier to access and use cryptocurrencies, while cold wallets were developed to provide more secure long-term storage.
Examples of Hot and Cold Wallets
Examples of hot wallets include:
Coinbase Wallet: A mobile wallet that is built into the Coinbase cryptocurrency exchange.
MyEtherWallet: A web-based wallet that is used for storing Ethereum and other ERC-20 tokens.
Examples of cold wallets include:
Ledger Nano S: A hardware wallet that supports a wide range of cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin.
Trezor: A hardware wallet that supports a wide range of cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Ripple.
How Hot and Cold Wallets Work
Hot wallets work by storing your private keys on a device that is connected to the internet. This makes it easy to access and use your cryptocurrencies, but also makes it more vulnerable to hacking and theft.
Cold wallets work by storing your private keys on a device that is not connected to the internet. This makes it more secure than a hot wallet, but also makes it more difficult to access and use your cryptocurrencies.
How to Use Hot and Cold Wallets
To use a hot wallet, you simply need to sign up for a cryptocurrency exchange or download a mobile app that supports hot wallets. Once you have created an account, you can deposit cryptocurrency into your wallet and start using it for day-to-day transactions.
To use a cold wallet, you will need to purchase a hardware wallet and follow the instructions for setting it up. Once your hardware wallet is set up, you can transfer cryptocurrency into it and store it offline for long-term storage.
In conclusion, hot and cold wallets are two main types of cryptocurrency wallets that are used for different purposes. Hot wallets are used for day-to-day transactions and are more vulnerable to hacking and theft, while cold wallets are used for long-term storage and are more secure but more difficult to access. It's important to choose the type of wallet that is right for your needs and to follow best practices for securing your cryptocurrency.